What is bitcoin blockchain ? And how it works complete guide.
Bitcoin is the world’s first and most well known advanced money. It is decentralized and constrained by nobody. How can it function, and for what reason might you at any point trust it? All things considered, in the event that PCs can duplicate any record, for what reason might I at any point make duplicates of my bitcoins? Also, on the off chance that it isn’t constrained by any one focal party, what keeps me from making fashioning exchanges for bitcoins I don’t possess? So What is bitcoin blockchain. This article will make sense of in layman’s terms the way that Bitcoin works and give data on how the innovation backing Bitcoin can be utilized for business use cases past essentially a computerized cash.
Bitcoin works by tackling three record-saving difficulties without the requirement for a focal record manager like a bank:
- Proving ownership of bitcoins.
- Preventing tampering with records of past transaction.
- Providing an authoritative ledger of transactions that is trustworthy.
Challenge #1: Proving Ownership
The first challenge for Bitcoin is proving ownership. When the owner of a bitcoin publishes a transaction to the network, how do we know that it actually came from that bitcoin’s owner and not an imposter? The answer to this lies in computer encryption.
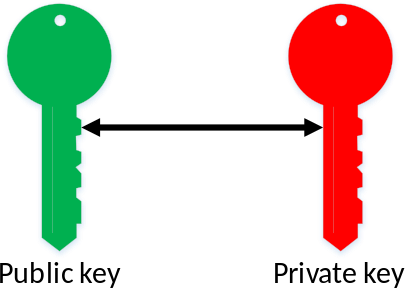
Public/Private Key Encryption
Bitcoin is based on a form of encryption called public/private key encryption. In this encryption, you generate two keys. Data encrypted with one key can be decrypted by the other and vice versa. One of these keys you make public and the other you keep a private secret.
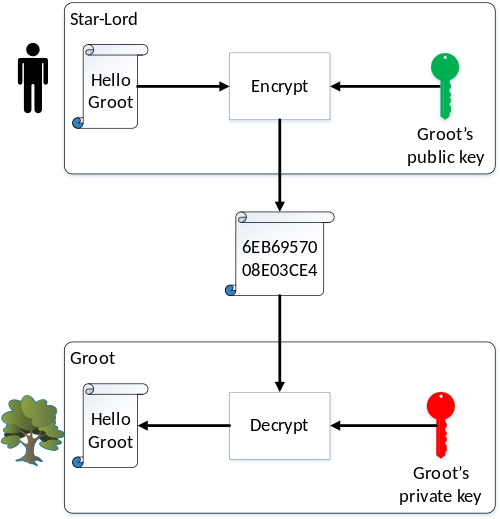
This opens the door for sending secret messages. Let’s use the characters from Guardians of the Galaxy for a fun example. Suppose that Star-Lord, the hero, wants to send a secret message “Hello Groot” to his tree-shaped friend Groot and ensure the movie’s arch-villain Thanos can’t read it. Groot has created a pair of public/private keys. Star-Lord takes Groot’s public key and uses it to encrypt the message. The message while in transit looks like gibberish, but when Groot receives it, his private key is able to decrypt it.
Digital Signing
Using these keys in reverse can also be used to verify the authenticity of who created the data, and that is how Bitcoin employs it. Now suppose Groot wants to send Star-Lord the message “I am Groot.” There is no reason to encrypt it because we all know that’s the only thing Groot says, but Groot wants to prove to Star-Lord that the message indeed came from Groot, not some 3rd party imposter. Groot would encrypt the message with his own private key. When Star-Lord receives the message and decrypts it with Groot’s public key, he sees “I am Groot.” This message is not a secret, but the fact that Groot’s public key decrypted it is proof that it was generated using Groot’s private key. Thus it proves the authenticity of the message.
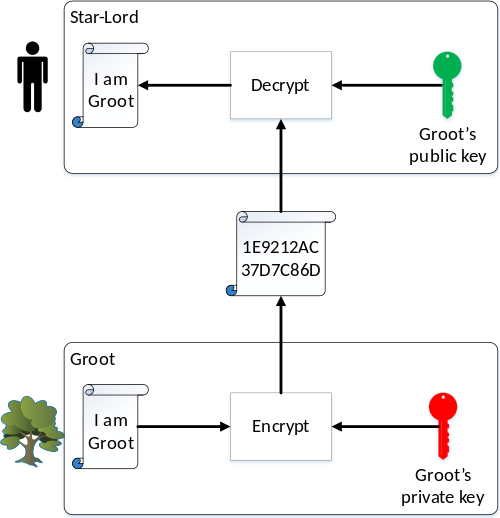
Signing Bitcoin Transactions
Bitcoin wallets are in fact public/private key pairs. When someone gives you his wallet ID, that ID is actually his public key. When you send coins to another wallet, the Bitcoin software uses your public key to authenticate that the transaction came from you, not an imposter.
If Groot wanted to send a bitcoin in his wallet to Star-Lord, he would generate a message declaring he’s transferring the bitcoin to Star-Lord’s wallet and use his private key to sign the message. So long as everyone agrees that the bitcoin being transferred indeed belonged to Groot’s public key wallet, the fact his public key can decipher this transaction proves Groot created this transaction. If Thanos instead forged a message claiming Groot sent him the bitcoin, everyone would know it was a fake since Groot’s public key would not be able to decipher any transactions written by Thanos.
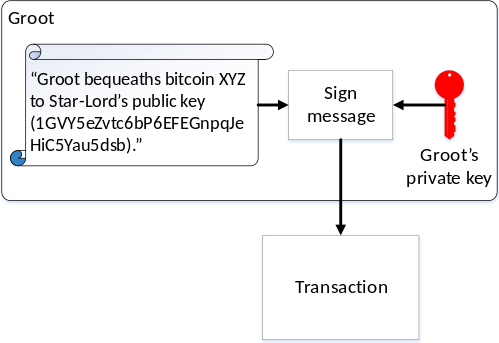
Bitcoin is essentially just a ledger of entries saying who transferred how many bitcoins to whom, all digitally signed by their owners. This much is like a financial ledger on paper with handwritten signatures authorizing each entry. When you send someone bitcoins, your signed transaction is appended to this ledger.
Challenge #2: Tampering with the Ledger
The next challenge is how to prevent tampering with the ledger. For example, if I send bitcoins to a friend, then a month later regret it, what’s to prevent me from going back and deleting the transaction from the ledger or changing the amount I had sent? This is dealt with using something called hashing.
Hashing
A hash is an algorithm for validating the integrity of data. Any message can generate a hash value, but small changes in the message result in radical changes in the hash value. For example, here are two messages and their hash values:
My name is Satoshi Mooter FE100DDA6D28B2280B34FC228ADAB42E
My name is Satoshi Mooter 1761420899A8F0B731A2EE56A6F71567
Suppose you are looking at an archive of a message I wrote My name is Satoshi nakamoto. If you know in advance that this message I wrote in the past had a hash value of FE100DDA6D28B2280B34FC228ADAB42E, you can then validate the message wasn’t tampered with by confirming it does indeed generate that hash. If someone tampered with this record changing it to My name is Satoshi nakamoto, then you would get the hash value 1761420899A8F0B731A2EE56A6F71567 and know someone had tampered with it.
The “Bitcoin Blockchain”
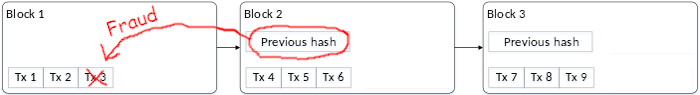
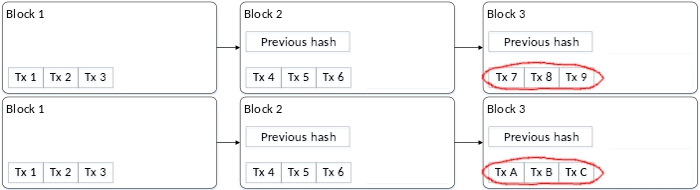
Bitcoin uses hashes to validate its ledger has not been tampered with. Periodically a collection of transactions are published together as one new record, called a block. Each block stores the hash of the block of transactions that preceded it. For example, take the transactions shown in this ledger of three blocks, each of which recorded three transactions labelled tx 1 through tx 9.

If I went back to delete transaction 3 from the first block, everyone would know that’s invalid because the hash in block 2 would prove block 1 was tampered with.
Fine, then I will also edit block 2 to have a hash that validates my forged block 1. This doesn’t work, either, because the hash value in block 2 that I just modified was an input to generate block 3’s validation hash, so now block 3’s hash reveals that block 2 has been tampered with.
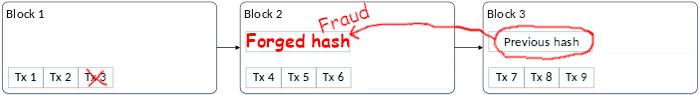
In sum, modifying one piece of the ledger is impossible: tampering with one transaction would require modifying the hash value of every block of transactions that followed it, which means generating a whole new ledger. This is why it is called blockchain: it is as though all the blocks are tightly chained together and cannot be unlinked from each other.
Challenge #3: Which Ledger is the Correct One
Even though one particular blockchain ledger is tamper-proof, what’s to prevent me from creating alternative competing ledgers? How do we know which ledger is the trusted one?
For example, suppose our blockchain has two blocks. Then I publish three new transactions appended to the ledger, but at the same time, I additionally publish three alternate transactions also appended to the ledger. Now we have two competing blockchains.
Proof of Work
This is solved through a concept called proof of work. Computers convert the hash values I described in the previous section into a sequence of zeros and ones like this:
0010111011110100000001000001101010010010001011101111100001001010
Suppose we imposed a constraint that a block cannot be added to the ledger unless the hash validating the previous block starts with a zero, then we would have a 1/2 chance of getting a hash that works.
0XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
Similarly, if we imposed a constraint that it must start with two zeros, then there would be a 1/4 chance. (We’d accept 00 but reject 01, 10, and 11.)
00XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
This grows exponentially. For example, if the constraint is that it must start with 32 zeros, then there would be approximately a 1 in 4 billion chance.
00000000000000000000000000000000XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
Bitcoin imposes such a constraint. Yet the hash of the previous block will always be constant. How do you get a hash that meets this constraint with a fixed input? By adding a random arbitrary value to every block. This is known as a “nonce” value.
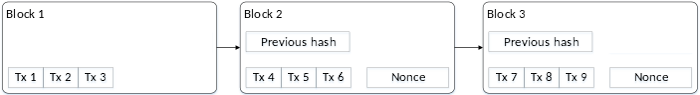
This nonce is combined with the previous block when computing the hash. Before adding a block to the ledger, computers around the world churn through random values searching for a nonce value that, when combined with the previous block, results in a hash that starts with a certain number of zeros. Finding that nonce value is the “proof of work.” (Incidentally, when a computer finds a hash that can be published, it includes a wallet, and that wallet is awarded free bitcoins. That is how new bitcoins are generated.)
This is so computationally intense that we can predict on average how long it will take. In Bitcoin’s case, it is one block every 10 minutes on average. Computers get more powerful as time progresses, so Bitcoin increases the difficulty to keep pace with advancing computer speeds by requiring more zeros every time a certain number of blocks is published.

Longest Ledger is the Oldest
Since proof of work makes it impossible to publish new blocks faster than a certain rate, we know that any ledger that is longer than another is also older. It would be impossible for me to produce a blockchain ledger that is longer than the official one unless I had more computing power at my personal disposal than the whole rest of all bitcoin users combined.
In sum, when there are competing ledgers on the Internet, all Bitcoin users recognize the one with the most blocks as the oldest and therefore authentic ledger.
Beyond Bitcoin
So there you have an explanation of Bitcoin in three easy steps:
- Digital signatures validate the ownership of bitcoins.
- Hashes validate the integrity of transactions listed on the ledger.
- Proof of work prevents the creation of rogue ledgers.
Hopefully, you can see that Bitcoin is simply a decentralized ledger that all users can trust. That ledger doesn’t have to just store currency. Other blockchains can and have been developed to allow multiple parties to share information without a central middleman broker. Some examples include:
- Counterfeit prevention. A product can have a bar code stamped on it by the manufacturer, who also records it on a blockchain. Every time the physical good changes hands, the owner also records this transfer on the blockchain. So long as you can trace your product back to a creation record from a known trusted manufacturer, you can be confident you got the real product, not a forgery. This is especially helpful for counterfeit pharmaceuticals, which is a growing black market that endangers lives.
- Logistics. Similar to counterfeit prevention, companies with complex supply chains of numerous competing suppliers can create a curated blockchain for tracking supplies. By curated, I mean some central company like Ford or Walmart controls who is allowed on the blockchain, limiting it to companies involved in their supply chain. This can be especially helpful for supply chains that have several layers of small parts suppliers feeding medium-sized parts suppliers feeding large-sized parts suppliers feeding the final manufacturer. A disruption at the small parts supplier could disrupt the final manufacturer, but with instant visibility to the whole supply chain, the manufacturer and suppliers can detect disruption at the earliest time possible and react to it sooner.
- Mutual cooperation. An auto insurance claim often involves two or more insurance companies that need to cooperate and share data. RiskStream is a blockchain designed to allow insurance companies to share trusted information with each other so that when there is a claim, the insurers do not need to go through manual data exchanges. This could both improve the customer experience by resolving claims sooner and also reduce claims processing costs by automating this manual data exchange process.
Blockchain for Business Value
There has been much hype about blockchains in the past several years. Much of that hype has been overblown. A challenge with blockchain is the fact your business cannot control it. Many companies are looking for ways to rapidly transform themselves and create new innovations their competitors can’t match. A blockchain protocol, in contrast, cannot be changed unless all participants agree to the change. This stifles it as a tool for digital transformation.
Another challenge is who bears the investment cost. Why should my company develop a blockchain that allows everyone in my industry to cooperate better? I would bear all the costs while the benefits would be diffused among all my competitors. This limitation makes curated blockchains more promising, since then the company that bears the cost of creating it can control it to ensure they reap the maximum benefits from that investment.
Finally, data protection and right to be forgotten laws create a challenge to blockchains. The data in them is immutable. How do you delete data from a blockchain if legal regulation requires it? There are solutions to that, but that is beyond the scope of this article.
Yet despite these challenges, blockchain can provide business value. What all of these use cases, from Bitcoin to RiskStream, have in common is that they build a trusted information exchange between parties who may not know each other and may even compete with each other. The key to successfully leveraging blockchain for your business is finding use cases that fit that pattern. Then design a blockchain solution that ensures your organization reaps the value you need, that the parties you need to participate in it are willing, and that you have proper plans in place for making blockchain data compliant with current or future data privacy laws.